Steel pipe flanges are essential components used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in a piping system. They provide flexibility for maintenance, inspection, or modification of pipelines by allowing easy assembly and disassembly. Depending on the application, pressure rating, and medium, different types of flanges are used—each designed to ensure a secure, leak-proof, and durable connection.
1. Weld Neck Flange (WN Flange)

Overview
The Weld Neck Flange features a long tapered hub that gradually transitions to the wall thickness of the pipe. It is welded circumferentially to the pipe, providing a strong and reliable connection.
Applications
Ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature, or critical service environments such as refineries, chemical plants, and power generation systems.
Material & Standards
-
Materials: Carbon Steel (A105), Stainless Steel (304/316/321), Alloy Steel (F11/F22), Duplex (2205).
-
Standards: ASME B16.5, ASME B16.47, DIN EN 1092-1, GOST, JIS B2220.
-
Pressure Ratings: Class 150 to Class 2500 / PN10–PN420.
Key Advantages
-
Excellent stress distribution between pipe and flange.
-
Reduces turbulence and erosion at the joint.
-
Preferred choice for severe service conditions.
2. Slip-On Flange (SO Flange)
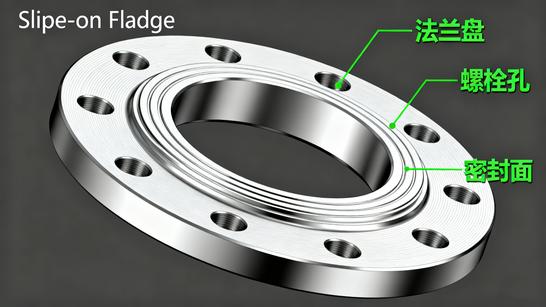
Overview
The Slip-On Flange is designed to slide over the end of a pipe before welding. It is typically fillet-welded on both the inside and outside for strength.
Applications
Common in low-pressure, non-critical systems such as cooling water lines, compressed air lines, and fire-fighting systems.
Material & Standards
-
Materials: Carbon Steel (A105), Stainless Steel (304/316), Galvanized Steel.
-
Standards: ASME B16.5, EN 1092-1, BS4504, ISO 7005-1.
-
Pressure Ratings: Class 150 / PN10–PN40.
Key Advantages
-
Easy to install and align.
-
Cost-effective for large-diameter pipelines.
-
Suitable for moderate corrosion and temperature conditions.
3. Blind Flange (BL Flange)
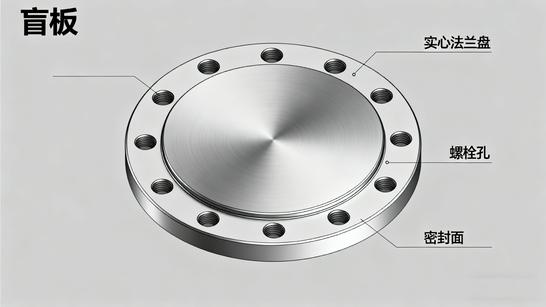
Overview
A Blind Flange has no bore and is used to close or isolate the end of a piping system, valve, or vessel opening. It can be easily removed to access the interior of the pipeline.
Applications
Used in pressure vessel ends, piping maintenance, and hydrostatic testing. Essential in systems that require frequent inspection or cleaning.
Material & Standards
-
Materials: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Duplex.
-
Standards: ASME B16.5, EN 1092-1, JIS B2220.
-
Pressure Ratings: Class 150–2500 / PN6–PN420.
Key Advantages
-
Provides a secure seal to stop flow.
-
Can handle high internal pressure.
-
Reusable in maintenance operations.
4. Socket Weld Flange (SW Flange)

Overview
The Socket Weld Flange is designed with a socket where the pipe is inserted and fillet welded around the hub. It is mainly used for small-diameter, high-pressure piping.
Applications
Ideal for chemical, petrochemical, and hydraulic systems where strength and leakage prevention are crucial.
Material & Standards
-
Materials: A105, F304/F316, F11, F22.
-
Standards: ASME B16.5, MSS SP-44.
-
Pressure Ratings: Class 300–1500.
Key Advantages
-
Smooth internal bore minimizes flow restriction.
-
High fatigue strength due to internal socket weld.
5. Threaded Flange (TH Flange)

Overview
The Threaded Flange (Screwed Flange) has internal threads that match external threads on a pipe. It allows assembly without welding—useful in systems where welding is not practical.
Applications
Widely used in low-pressure, flammable, or explosive environments such as fuel pipelines and small-diameter air systems.
Material & Standards
-
Materials: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Brass, Galvanized Steel.
-
Standards: ASME B16.5, EN 1092-1.
-
Pressure Ratings: Class 150–600.
Key Advantages
-
Easy installation and removal.
-
Ideal for temporary or maintenance-prone systems.
6. Lap Joint Flange (LJ Flange)

Overview
The Lap Joint Flange is used with a stub end. The flange itself is not welded to the pipe but slides over the stub end, allowing for easy alignment and disassembly.
Applications
Common in low-pressure, non-critical, or corrosive environments such as water treatment and food processing.
Material & Standards
-
Materials: Carbon Steel (A105), Stainless Steel (304/316), Alloy 400.
-
Standards: ASME B16.5, EN 1092-1.
-
Pressure Ratings: Class 150–300 / PN6–PN40.
Key Advantages
-
Economical for systems requiring frequent dismantling.
-
Reduces material cost when used with expensive stub-end alloys.
7. Orifice Flange (OF Flange)

Overview
The Orifice Flange set is designed with pressure tap holes for flow measurement. When paired with an orifice plate, it helps measure the rate of fluid flow in pipelines.
Applications
Used in flow monitoring systems, oil & gas metering, and industrial process control.
Material & Standards
-
Materials: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Duplex Steel.
-
Standards: ASME B16.36, API 605.
-
Pressure Ratings: Class 300–1500.
Key Advantages
-
Enables accurate flow measurement.
-
Integrates easily into existing flange connections.
Material Selection and Standard Compliance
Selecting the right flange material and standard is crucial to ensuring safe, long-term operation.
| Environment | Recommended Material | Relevant Standard |
|---|---|---|
| High temperature & pressure | Alloy Steel (F11/F22), Stainless Steel 321 | ASME B16.5, ASTM A182 |
| Corrosive media (acid, seawater) | Stainless Steel 316L, Duplex 2205 | ASME B16.5, EN 1092-1 |
| General water or air system | Carbon Steel A105 | ASME B16.5 |
| Cryogenic service | Stainless Steel 304L, 316L | ASME B16.5 |
Conclusion
Steel pipe flanges are far more than simple connectors—they are vital to the safety, reliability, and serviceability of modern piping systems. Understanding the types, material standards, and applications ensures better selection and long-term system performance.
Whether your project involves oil & gas pipelines, chemical process systems, or water treatment infrastructure, choosing the right flange type and material is key to achieving efficiency, durability, and compliance with global standards.




